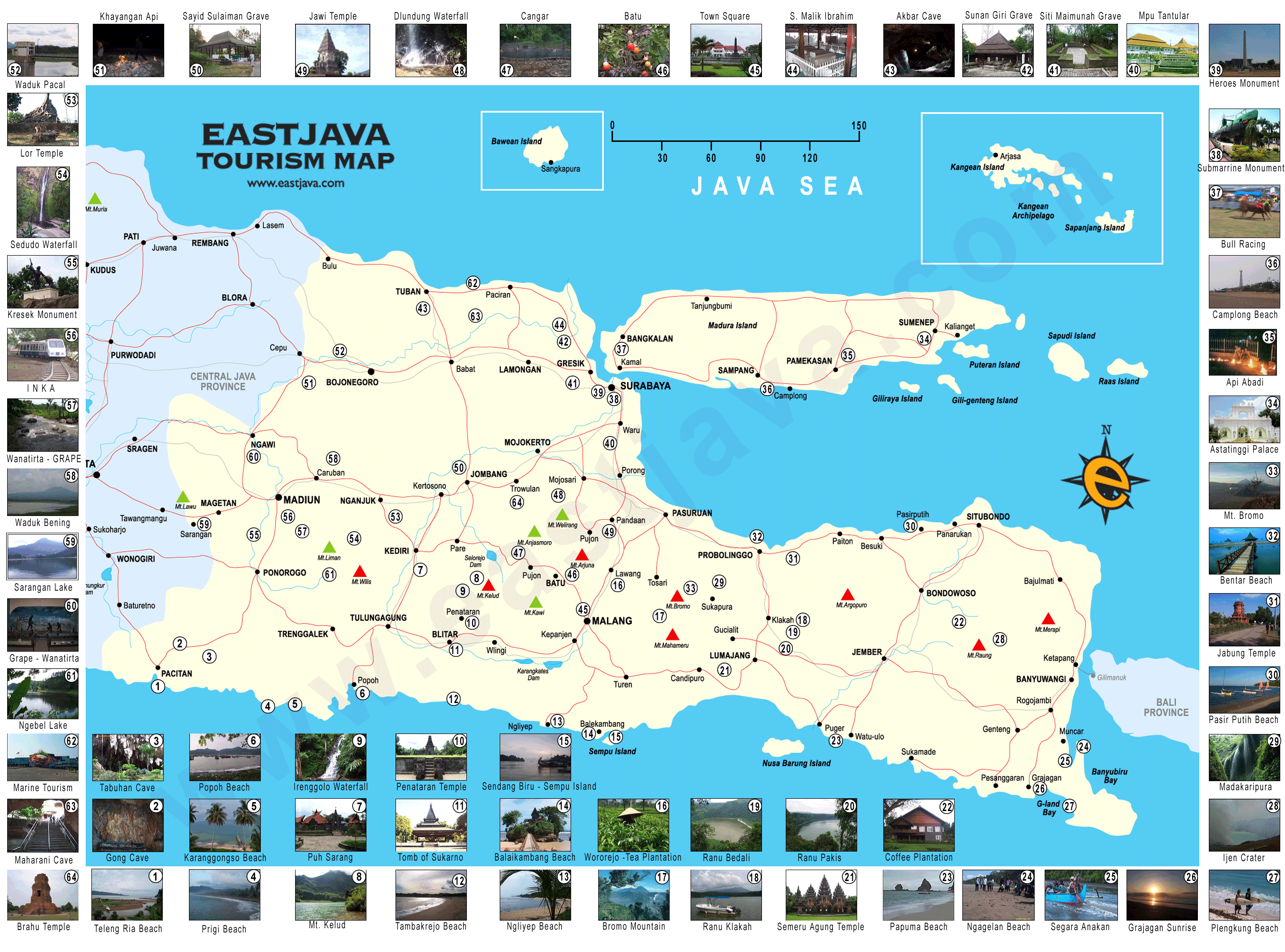
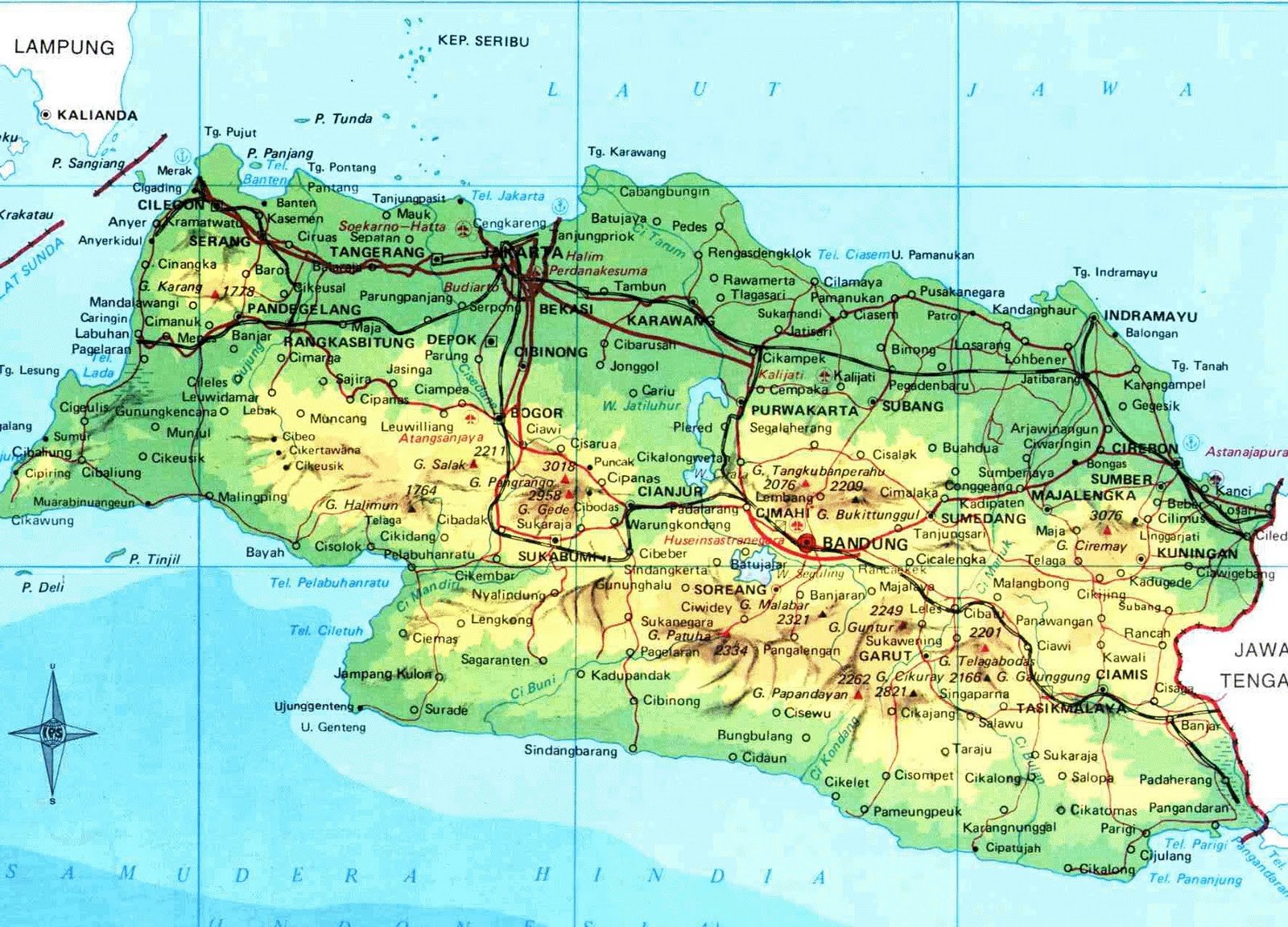
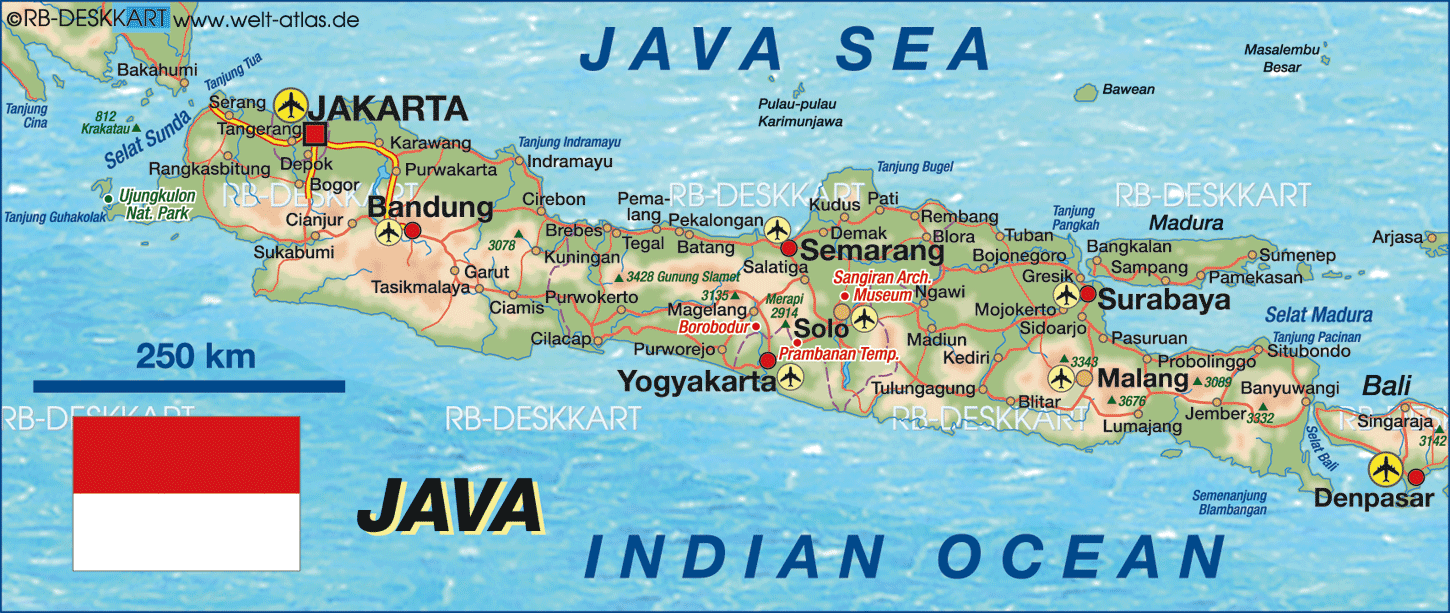
What Map In Java. A map is a key-value mapping, which means that every key is mapped to exactly one value and that we can use the key to retrieve the corresponding value from a map. Java Map interface is not a subtype of the Collection interface. The Java platform contains three general-purpose Map implementations: HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap. Why do we need a HashMap? A HashMap however, store items in " key / value " pairs, and you can access them by an index of another type (e.g. a String ). HashMap and LinkedHashMap allow null keys and values, but TreeMap doesn't allow any null key or value.

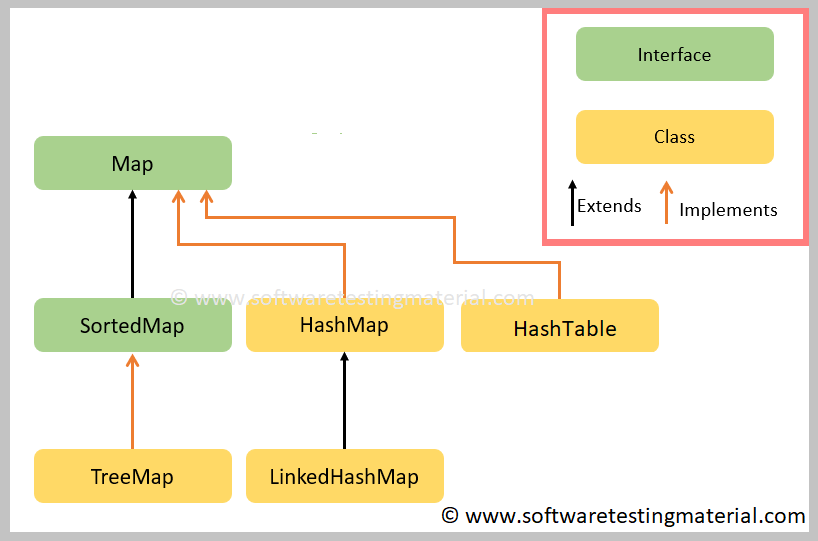
What Map In Java. Each key maps to a value hence the name. Read Discuss Practice In Java, Map Interface is present in java.util package represents a mapping between a key and a value. The hierarchy of Java Map is given below: A Map doesn't allow duplicate keys, but you can have duplicate values. Data is stored in key-value pairs with every key being unique. Java HashMap is similar to HashTable, but it is unsynchronized. HashMap class declaration Let's see the declaration for java.util. What Map In Java.
The hierarchy of Java Map is given below: A Map doesn't allow duplicate keys, but you can have duplicate values.
HashMap class. public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable HashMap class Parameters What is HashMap?
What Map In Java. Map package in order to use Map. Why do we need a HashMap? However, in this article, we'll dig a bit deeper and explain why interfaces are useful. The Java platform contains three general-purpose Map implementations: HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap. A HashMap however, store items in " key / value " pairs, and you can access them by an index of another type (e.g. a String ). HashMap class declaration Let's see the declaration for java.util.
What Map In Java.