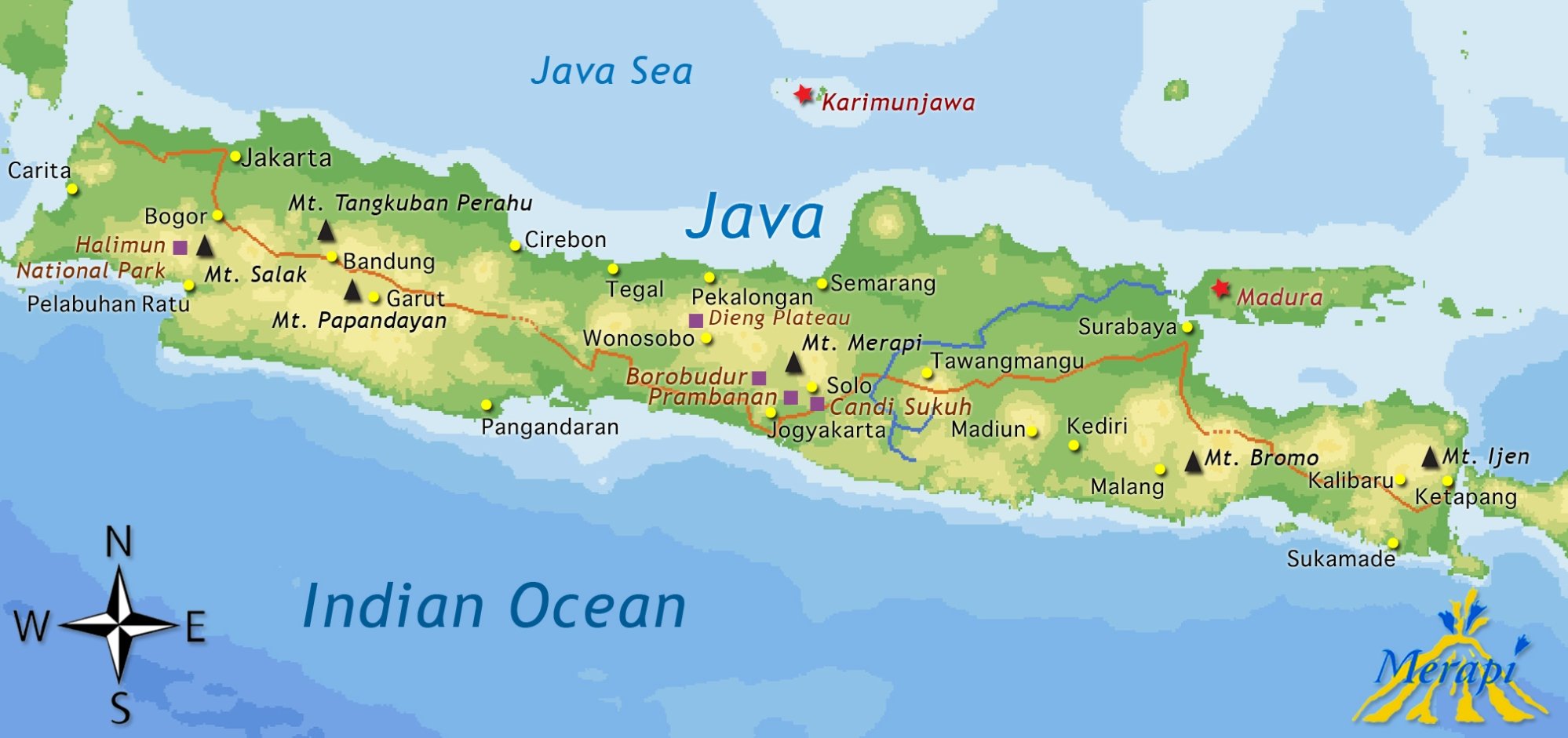
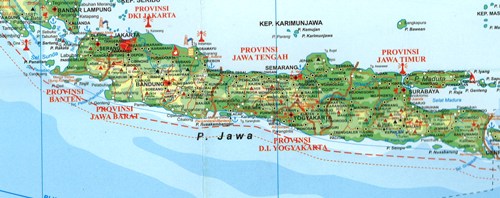
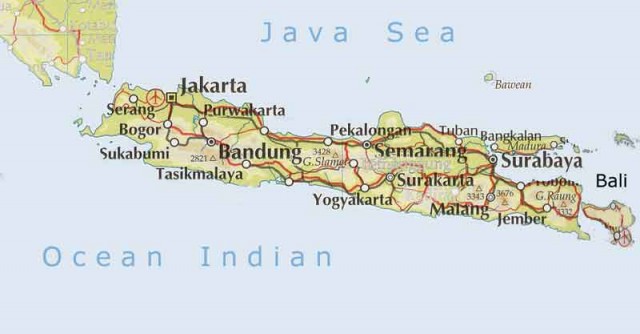
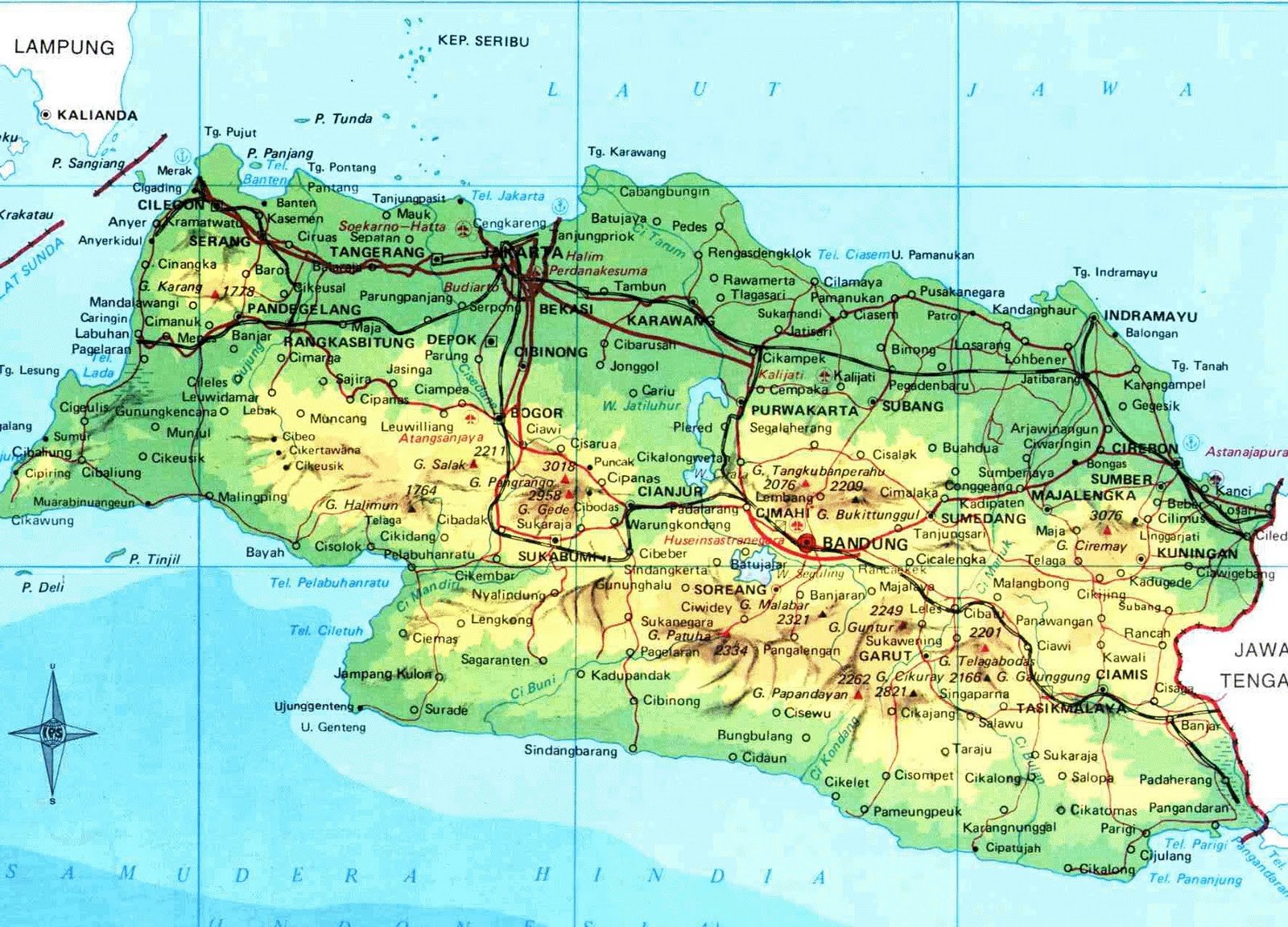
For Map In Java. Please refer to a couple of our other articles to learn more about the java.util. Stream API should be used when we're planning on doing some additional Stream processing; otherwise, it's just a simple forEach() as described previously. Let's take entrySet() as the example to see how Stream API works:. public void iterateUsingStreamAPI(Map<String, Integer> map. A class very similar to HashMap is Hashtable. Overview In this article, we'll see how to use HashMap in Java, and we'll look at how it works internally. We can use this feature to loop through a Map as well.
For Map In Java. Methods in Java Map Interface Example: Java import java.util.*; class GFG { public static void main (String args []) { Map<String, Integer> hm Java HashMap In the ArrayList chapter, you learned that Arrays store items as an ordered collection, and you have to access them with an index number ( int type). Map in Java is an interface available in java.util package and it stores the data in key and value pairs. NavigableMap ConcurrentMap Java Map Subinterfaces How to use Map? Let's take entrySet() as the example to see how Stream API works:. public void iterateUsingStreamAPI(Map<String, Integer> map. However, this doesn't mean that we can't convert a Map structure into different sequences which then allow us to work in a natural way with. Please refer to a couple of our other articles to learn more about the java.util. For Map In Java.
The hierarchy of Java Map is given below: A Map doesn't allow duplicate keys, but you can have duplicate values.
I am trying to map a json string to my user defined class DataDeletionRequest.
For Map In Java. Their behavior and performance are precisely analogous to HashSet, TreeSet, and LinkedHashSet, as described in The Set Interface section. Map in Java is an interface available in java.util package and it stores the data in key and value pairs. The difference between Map and HashMap is that the first one is an interface, and the second is an implementation. We first import the desired instructions, along with `HashMap` and `Map`, which are part of the Java `util` package deal. Data is stored in key-value pairs with every key being unique. Let's take entrySet() as the example to see how Stream API works:. public void iterateUsingStreamAPI(Map<String, Integer> map.
For Map In Java.